The growth of plants requires large amounts of water and fertilizers to provide nutrients, and these effects are achieved through the roots of the plants. The more developed the root system of plants, the more lush the foliage, and vice versa, the leaves are yellow, the growth and germination are poor, and the crops There is a close relationship between the yield of the plant and the root morphology of the plant. Therefore, analyzing the morphological characteristics of the plant roots with the aid of the root analyzer is of great significance for the development of modern precision agriculture and the high yield and quality of crops.
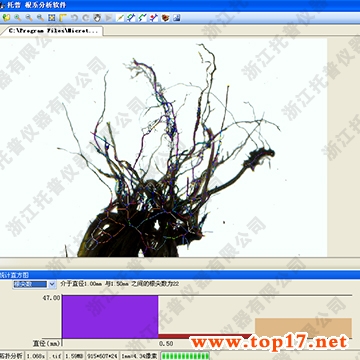
The growth of the root system is often related to the soil moisture environment. This is the main reason why the same crop has a large difference in the growth of different plots. Phosphorus fertilizer is a common type of fertilizer in agricultural production. The appropriate amount of phosphate fertilizer is helpful for the growth of plants, but excessive phosphate fertilizer may cause pollution to the agricultural environment. Therefore, the current development of ecological agriculture requires that the utilization rate of phosphate fertilizer be increased. While exploring the genetic potential of the crop's own phosphorus nutrients, improving the nutrient shape of crops has become a major way to increase the utilization of phosphate fertilizers. Root analysis is used to analyze the root morphology of rice under low-phosphorus stress to reveal the differences in rice phosphorus uptake characteristics. The mechanism is of great significance.
The test results obtained with the root analyzer showed that under low phosphorus stress, the total root number, total root length, total root surface area, root length, lateral root number, and lateral root density of the low phosphorus-tolerant varieties were all significantly increased, while low Phosphorus-sensitive cultivars showed no significant changes in lateral root density, but other parameters were significantly reduced. Studies have shown that the root characteristics of plants have a decisive role in obtaining phosphorus nutrition. Root surface area, total root length, lateral root length, and lateral root number are positively correlated with phosphorus uptake. The strong root system of the low phosphorus-tolerant varieties promoted their higher mineral element uptake under low phosphorus conditions, while the higher nutrient content promoted the growth of rice.
Titanium Nut,Titanium Flange Nut,Titanium Alloy Nut Flange,Titanium Hexagon Flange Nut
Baoji Qiyuexin Metal Material Co., Ltd. , https://www.qyxtitanium.com