How to properly use the flotation reagent, that is, how to correctly determine the problem of the pharmaceutical system before flotation. The pharmaceutical system refers to the type of agent, dosage, method of addition, location of dosing, and dosing sequence added during the flotation process. The chemical system and ore properties of the flotation plant, process flow, and several mineral processing products are required. related. It is usually determined by optional tests or semi-industrial tests of the ore. The pharmaceutical system is an important factor affecting the economic indicators of mineral processing technology .
1, the type of medicine
The type of drug used in the flotation plant is related to the nature of the ore, the process, and the need to obtain several mineral processing products. It is usually determined by optional tests or semi-industrial tests of the ore.
The types of drugs are classified according to the action of the drugs, and can be roughly classified into three categories.
(1) Foaming agent: an organic surface active substance distributed on the water-air interface. It is used to produce a foam layer which can float minerals. The foaming agent is pine oil, cresol oil, alcohol and the like.
(2) Collector : Its role is to capture the mineral of interest. The collector can change the hydrophobicity of the mineral surface and make the floating mineral particles adhere to the bubbles. According to the nature of the action of the drug, it is classified into a non-polar collector, an anion collector, and a cation collector. Commonly used collectors are black medicine, xanthate, white medicine, fatty acid, fatty amine, mineral oil and the like.
(3) Conditioning agent: The adjusting agent includes an activator and an inhibitor, changes the properties of the surface of the ore, affects the action of the mineral and the collector, and the adjusting agent is also used to change the chemical or electrochemical properties of the aqueous medium, for example, changing the pH. The value and the state of the collector. There â‘ pH value adjuster adjusting agent: lime, sodium carbonate, sulfuric acid, sulfur dioxide; â‘¡ activator: copper sulfate, sodium sulfide; â‘¢ inhibitors: lime, ferrocyanide, sodium sulfide, sulfur dioxide, sodium cyanide, zinc sulfate, heavy chromium, potassium waterglass, tannin, soluble gums, starches, synthetic polymers and the like; â‘£ other: wetting agents, floating agents, solubilizers and the like.
2, dosage:
When the flotation is used, the dosage of the agent should be just right. The insufficient or excessive amount has an effect on the beneficiation index. If the dosage is too large, the ore dressing cost will increase.
Relationship between the dosage of various chemicals and flotation index
Insufficient amount of collector, insufficient mineral hydrophobicity, reduced recovery rate, excessive drug quality, reduced concentrate quality, and difficulties in separation and flotation;
Insufficient amount of foaming agent, poor foam stability, excessive dosage, and “running†phenomenon;
The amount of activator is too small, the activation is not good, and the dosage is too large, which will destroy the selectivity of the flotation process;
Insufficient amount of inhibitor, low grade of concentrate, excessive amount of chemicals will inhibit the minerals that should be floated, and the recovery rate will decrease.
3, the drug configuration, the solid agent is diluted into a liquid, easy to add. Poorly water-soluble agents such as xanthate, amine black medicine, water glass, sodium carbonate, copper sulfate, sodium sulfide, etc. are all formulated into aqueous solutions, and the concentration ranges from 2% to 10%. The water-insoluble agent is first dissolved in a solvent, and then formulated into an aqueous solution, such as an amine collector, and some may be directly added such as 2# oil, 31 black drug, oleic acid, and the like. For a drug that is easily soluble in water and used in a large amount, the concentration is generally 10 to 20%, and if sodium sulfide is used, it is formulated to be 15%. For a poorly water-soluble agent, it can be dissolved by means of an organic solvent and then formulated into a low concentration solution.
The choice of the formulation method of the medicament is mainly based on the nature of the medicament, the addition method and function. The same agent, due to different preparation methods, the amount and effect are very different, generally the usual preparation methods are:
1 formulated into 2% to 10% aqueous solution, most of the water-soluble agents are formulated (such as xanthate, copper sulfate, water glass, etc.)
2 Solvent preparation, some water-insoluble agents, can dissolve the agent in a special solvent, for example, the white drug is insoluble in water, but soluble in 10% to 20% aniline solution, after being prepared into an aniline mixed solution, Use; for example, aniline black medicine is insoluble in water, but soluble in alkaline solution of sodium hydroxide, so when using aniline black medicine, first prepare an alkaline solution of sodium hydroxide, and then add the agent to prepare aniline. The black drug solution is added to the flotation machine.
3 Formulated as a suspension or emulsion, for some non-soluble solid agents, can be formulated into an emulsion. If the solubility of lime in water is small, the lime can be ground into a powdery suspension with water (for example, lime milk), or it can be directly added to the ball mill and the mixing tank in a dry powder form.
â‘£ saponified fatty acids for the collector, the saponification is the most common method, such as when selected from hematite, oxidized paraffin used in conjunction with soaps and tall oil as collector. In order to saponify the Tal oil, when the agent is formulated, about 10% of sodium carbonate is added, and heated to form a hot soap solution.
5 Emulsification, emulsification is carried out by ultrasonic emulsification or mechanical strong agitation. If fatty acids and diesel oil are emulsified, they can increase their dispersion in the pulp and improve the effect of the agent. Adding a part of the emulsifier has a better effect. Many surface active substances can be used as emulsifiers.
6 Acidification, when using cationic collectors, because of its poor solubility, it must be pretreated with hydrochloric acid or acetic acid before it can be dissolved in water for flotation.
7 Aerosol method is a new preparation method for strengthening the action of the medicament. Its essence is to use a special spray device to directly atomize the medicament into the flotation tank after atomizing it in the air medium. So it is also called "aerosol flotation method". This method not only improves the floatability of the useful minerals, but also significantly reduces the amount of the agent. For example, the collector is only 1/3 to 1/4 of the usual amount, and the amount of the foaming agent is only 1/5.
8 Electrochemical treatment of the agent, in the solution, the chemical treatment of the flotation agent by direct current can change the state of the agent itself, the pH value of the solution and the value of the redox potential, thereby increasing the component of the most active agent. The concentration increases the critical concentration of colloidal particles and increases the degree of dispersion of poorly soluble agents in water.
Usually, the collector and foaming agent are stirred for 1-2 minutes, while some chemicals need to be stirred for a long time. For example, copper and lead are separated by potassium dichromate to inhibit lead.
4, dosing location, in order to sufficiently exert effects of flotation agents, dosing location is general practice: adjusting agent, inhibitor and collector portion (e.g., coal oil) was added in a ball mill so as to cause a suitable float as soon as possible Choose the environment. The collector and foaming agent are added to the first mixing tank of the flotation. If the flotation operation has two mixing tanks, the activator should be added to the first mixing tank, and the collector and foaming agent should be added to the second mixing tank. . The location of addition varies depending on the role of the agent in the flotation machine. Such as copper sulfate, xanthate, pine oil oil three agents, the general dosing sequence copper sulfate added in the center of the first stirred tank, xanthate added in the center of the second stirred tank, pine oil added to the second stirred tank exit. In the general case, the flotation plant first adds the pH adjuster to adjust the slurry to a suitable pH value to better play the role of the collector and the inhibitor. When adding a drug, be aware that certain harmful ions cause the problem of drug failure. For example, the reaction of copper ions with hydride ions will cause the hydride to fail. When copper and sulfur are separated, if more copper ions appear in the stirred tank, do not add cyanide to the stirred tank, but should be added directly to the separation tank. Choose the job.
5. Dosing sequence: The general dosing sequence of the flotation plant is: the flotation of the ore should be: pH adjuster, inhibitor or activator, foaming agent, collector, and flotation suppressed. Minerals are: activators, collectors, foaming agents.
6, dosing method: usually there are two types of concentrated addition and dispersion. The general principle is: for those that are easily soluble in water, not easily taken away by the foam, and the agents that are not easy to be inactivated can be added centrally, that is, all the agents are concentrated and added once before rough selection. Conversely, for those agents that are easily removed by the foam and that are easily disabled by the action of fine mud and soluble salts, they should be added in stages. The regulator, the inhibitor and a part of the collector (such as kerosene) are added to the ball mill, and the collector and the foaming agent are added to the first mixing tank of the flotation. If there are two mixing tanks in the flotation operation, the An agitating tank is added with an activator, and a second mixing tank is added with a collector and a foaming agent (such as zinc flotation).
In order to improve the efficacy of the medicament and save the dosage of the medicament, in recent years, many experimental research work has been carried out in the application of physical methods to enhance the efficacy of the medicament. Among them are emulsification, warm flotation, aerosol method, electric field and magnetic field treatment, ultraviolet radiation, high energy radiation to enhance the flotation process and the role of chemicals.
Engine powered winch introduction
Engine powered winch is set up high-voltage transmission lines and laying of aerial construction machinery underground cables, smooth, convenient for Tower Group legislature, set up guide (land) lines, lifting, pulling in a variety of complex conditions. Motor cutter grinding widely used in electricity, telecommunications line construction group established tower or motor actinomycetes, also in place for lifting and pulling heavy objects, suitable for field sites without electricity, the use of flexible construction, docks and so on. The experiments and field practice has proved that with a reasonable structure, small size, light weight, utilitarian large, flexible operation, easy handling, etc., the majority of electric power, telecommunications operators welcome. Motor cutter grinding force divided by diesel powered winch and winch motor gasoline.

Features:
1. Reasonable structure
2. Small volume
3. Light weight
4. Strong power
5. Nimble operation
6. Convenient transporting.
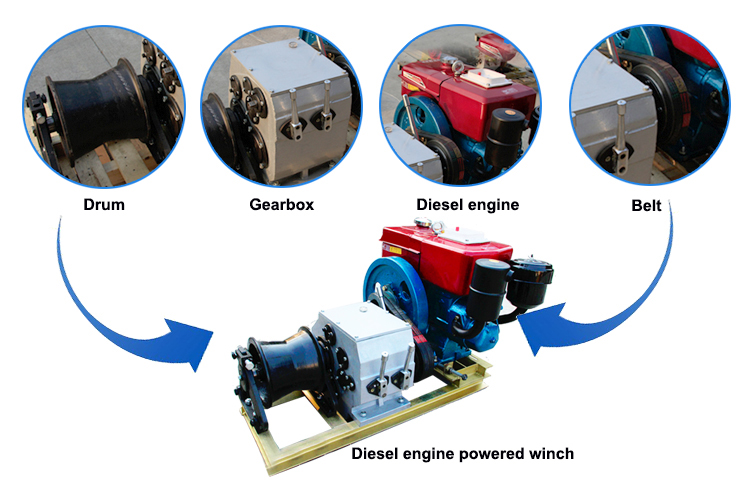
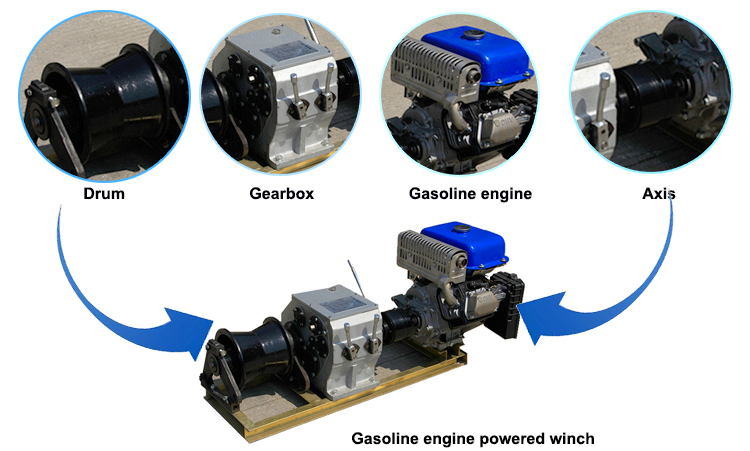
Engine powered winch type table:
|
Power |
Gasoline engine |
Air cooling |
|
Diesel engine |
Water cooling |
|
|
Air cooling |
||
|
Traction |
3t |
faster |
|
5t |
Faster slow |
|
|
8t |
slow |
|
|
Drive mode |
Belt drive |
|
|
Axis drive |
||
|
Starting mode |
Hand cranking |
|
|
Hand pulling |
||
|
Drums |
Single drum |
|
|
Double drum |
||
Engine Powered Winch,Electric Winch,Electric Winches,Small Electric Winch
Hebei Long Zhuo Trade Co., Ltd. , https://www.hblongzhuo.com