The temperature transmitter adopts thermocouple and thermal resistance as the temperature measuring element, and the output signal from the temperature measuring element is sent to the transmitter module, after filtering, arithmetic amplification, nonlinear correction, V/I conversion, constant current and reverse After the protection and other circuits are processed, it is converted into a 4-20mA current signal 0-5V/0-10V voltage signal that is linearly related to the temperature, and the RS485 digital signal is output.

A device that converts a physical measurement signal or an ordinary electrical signal into a standard electrical signal output or can be output as a communication protocol. The temperature transmitter is a meter that converts a temperature variable to a standard output signal that can be transmitted, and is mainly used for measuring and controlling temperature parameters of an industrial process. The current transmitter converts the AC current of the main circuit under test into a constant-current loop standard signal, which is continuously transmitted to the receiving device.
The temperature current transmitter converts the temperature sensor signal into a current signal and is connected to a secondary meter to show the corresponding temperature. For example, the model of the temperature sensor in the figure is PT100, then the function of the temperature and current transmitter is to convert the resistance signal into a current signal, input the meter, and display the temperature.
Isolated temperature transmitter:
* Execution standard: IEC688:1992, QB
 A40 temperature transmitter
A40 temperature transmitter
* Input range: -60°C~175°C
* Accuracy level: ≤0.5%.FS
* Total power consumption: ≤0.5VA
* Insulation resistance: ≥20MΩ(DC500V)
* Response time: ≤350mS
* Working environment: -10 °C ~ 50 °C, 20% ~ 90% non-condensing * Storage environment: -40 °C ~ 70 °C, 20% ~ 95% non-condensing
* Convert the measured ambient temperature isolation into a single standard DC voltage or DC current output in a linear ratio;
* Low power consumption and high reliability
* Excellent anti-interference ability;
* Plug and socket terminal interface, standard rail (35mm) installation;
* Small size, shape size (mm): 95 (L) × 37 (W) × 32 (H);
A temperature transmitter is a meter that converts a temperature variable to a standardized output signal that can be transmitted. It is mainly used for the measurement and control of industrial process temperature parameters.
Transmitters with sensors usually consist of two parts: sensors and signal converters. The sensors are mainly thermocouples or thermal resistors; the signal converters are mainly composed of measuring units, signal processing and conversion units (since the industrial thermal resistance and thermocouple index tables are standardized, the signal converters are also known as independent products. Transmitters) Some transmitters have additional display units and some also have fieldbus functionality. As the right picture:
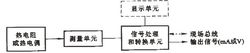 Temperature transmitter schematic
Temperature transmitter schematic
If the transmitter consists of two sensors for measuring the temperature difference, there is a given continuous function relationship between the output signal and the temperature difference. It is called a temperature transmitter.
There is a given continuous function relationship (usually a linear function) between the output signal of the transmitter and the temperature variable, and the output signal of the early production transmitter has a linear function relationship with the resistance value (or voltage value) of the temperature sensor. .
The standardized output signals are mainly 0mA~10mA and 4mA~20mA (or 1V~5V) DC signals. Other standardized output signals with special regulations are not excluded. The temperature transmitter can be divided into two-wire system and four-wire system according to the power supply connection mode, except that the RWB type temperature transmitter is a three-wire system.
Transmitters have electric unit combination meter series and miniaturized modular type, multi-function intelligent type. The former does not have a sensor, and the latter two types of transmitters can be easily combined with a thermocouple or a thermal resistor to form a sensor-equipped transmitter.
Petroleum, chemical, chemical fiber; textile, rubber, building materials; electricity, metallurgy, medicine; food field and other industrial field temperature measurement process control; especially suitable for computer measurement and control systems, but also supporting the use of instruments.
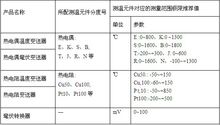
Types of
Temperature range (°C)
Minimum range (°C)
Absolute error
Basic error
K
0~1300
120
±1°C
±0.2%
E
0~1000
80
±1°C
±0.2%
S
0~1600
580
±3°C
±0.2%
B
400~1800
1,000
±3°C
±0.2%
R
0~1600
850
±3°C
±0.2%
T
-200~400
120
±1°C
±0.2%
N
0~1200
180
±3°C
±0.2%
W
0~2300
340
±3°C
±0.2%
J
0~1200
100
±3°C
±0.2%
1, thermocouple temperature transmitter technical indicators
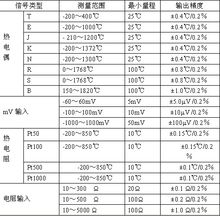
※enter
Input type: K, E, S, B, T, J, etc. thermocouples
Temperature range: (as shown below)
Input impedance: ≥20KΩ
Cold junction temperature compensation: -15 to +75°C
※Output
Output current: 4~20mA
Output loop power supply: 12~30VDC
Minimum operating voltage: 12VDC
The relationship between load resistance and power supply:
※ Comprehensive parameters
Standard accuracy: ±0.2%
Temperature drift: basic error/10°C
Thermal resistance lead compensation: ±0.1% (0~10Ω)
Impact of load change: ±0.1% (allowable load range)
Impact of power supply changes: ±0.1% (12 to 30V)
Power on response time: <1S (0~90%)
Working environment temperature: -20~+70°C
Protection class: IP00/IP54 (sensor protection level decision)
Electromagnetic Compatibility: Complies with IEC61000, EN61000
2, thermal resistance temperature transmitter technical indicators
※enter
Temperature range: Pt100:-200~850°C Cu50:-50~150°C
Minimum temperature range: 50°C
Lead resistance: ≤ 10Ω
※Output
Output current: 4~20mA
Output loop power supply: 12~30VDC
Minimum operating voltage: 12VDC
The relationship between load resistance and power supply:
Load Resistance (Including Lead Resistance) = Power Supply (V)-12(V)/0.02A
※ Comprehensive parameters
Standard accuracy: ±0.2% (see selection table) Note: Need high precision can be customized
Temperature drift: basic error/10°C
Thermal resistance lead compensation: ±0.1% (0~10Ω)
Impact of load change: ±0.1% (allowable load range)
Impact of power supply changes: ±0.1% (12 to 30V)
Power on response time: <1S (0~90%)
Working environment temperature: -20~+70°C
Protection class: IP00/IP54 (sensor protection level decision)
Electromagnetic Compatibility: Complies with IEC61000, EN61000
Figure
Modular Temperature Transmitter Outline Drawing
Rail Temperature Transmitter Outline Drawing
â— High precision
â— Range, zero external continuous adjustable
â— Good stability
â— Up to 500% positive migration and up to 600% negative migration
â— Two-wire system, three-wire system, four-wire system
â— Adjustable damping, over pressure resistance
â— Solid sensor design
â— No mechanical moving parts, less maintenance
â— Light weight (2.4kg)
â— All series of unified structure, strong interchangeability
â— Miniaturization (166mm total height)
â— Optional diaphragm material for contact with media
â— Unilateral overpressure
â— Low pressure cast aluminum alloy housing
â—Super measurement performance for pressure, differential pressure, level, flow measurement
â—Digital accuracy: +(-)0.05%
â— Analog Accuracy: +(-)0.75%+(-)0.1%FS
â— Full performance: +(-)0.25FS
â— Stability: 0.25% 60 months
â— Turndown ratio: 100:1
â— Measurement rate: 0.2S
â— Miniaturized (2.4kg) stainless steel flange, easy to install (see figure right)
â— The process connection is compatible with other products to achieve the best measurement
â— The only sensor (patented technology) using H alloy sheath in the world achieves excellent cold and thermal stability
â— Intelligent transmitter with 16-bit computer
Standard 4-20mA with digital signal based on HART protocol, remote control
â— Support upgrades to fieldbus and field-based control technology.
The temperature transmitter power supply must not have spikes, otherwise it is easy to damage the transmitter. The calibration of the transmitter should be performed 5 minutes after power up, and the ambient temperature should be taken into consideration. When measuring temperature (>>100°C), the sensor chamber is insulated from the junction box with a filler material to prevent the junction box from overheating the transmitter. If the sensor is used under severe interference conditions, the enclosure should be firmly grounded to avoid interference. The power and signal output should be transmitted using Ф10 shielded cable. The pressure nut should be tightened to ensure airtightness. Only the RWB type temperature transmitter has a 0~10mA output, which is a three-wire system. Below 5% of the range value, it is not linear due to the turn-off characteristics of the transistor. The temperature transmitter should be calibrated every 6 months. If the DWB cannot be linearly corrected due to circuit limitations, it is best to follow the instructions to select the range to ensure its linearity.
The reason for the incorrect display of data
1. Line length, signal attenuation;
2. Line impedance mismatch
3 signal interference, no shielding;
Integrated temperature transmitter
The integrated thermal resistance temperature transmitter is a relatively small temperature transmitter that can be mounted in a junction box of a thermal resistor. The integrated temperature transmitter generally consists of a temperature probe (thermocouple or RTD sensor) and a two-wire solid electronic unit. The solid-state module is used to mount the temperature probe directly in the junction box to form an integrated transmitter. Integrated temperature transmitters are generally classified into two types: thermal resistance and thermocouple type.
Thermal resistance temperature transmitter is composed of reference unit, R/V conversion unit, linear circuit, reverse connection protection, current limiting protection, V/I conversion unit and so on. After the temperature-resistor resistance signal is converted and amplified, the linear circuit compensates the nonlinear relationship between temperature and resistance. After the V/I conversion circuit, a constant-current signal of 4-20 mA which is in linear relationship with the measured temperature is output.
The thermocouple temperature transmitter is generally composed of a reference source, a cold junction compensation, an amplifying unit, a linearization process, a V/I conversion, a burnout processing, a reverse connection protection, and a current limit protection circuit unit. It is the thermal potential generated by the thermocouple through the cold-end compensation after amplification, and then cap the linear circuit to eliminate the thermal potential and temperature of the nonlinear error, and finally amplified into 4 ~ 20mA current output signal. In order to prevent accidents caused by temperature control failure due to galvanic disconnection in thermocouple measurement, a power failure protection circuit is also provided in the transmitter. When the thermocouple breaks or fails to connect properly, the transmitter will output the maximum value (28mA) to make the meter cut off the power.
The integrated temperature transmitter has the advantages of simple structure, saving lead wire, large output signal, strong anti-interference ability, good linearity, simple display instrument, solid module moisture resistance, reverse connection protection, current limiting protection, and reliable work.
The output of the integrated temperature transmitter is a unified 4-20mA signal; it can be used in conjunction with a microcomputer system or other conventional instruments. It can also be made into explosion-proof or fire-proof measuring instruments at the request of users.
Integrated installation form, compact size, cost-effective, economical and practical, output two-wire 4 ~ 20mA signal, according to the latest explosion-proof regulations in line with international IEC standards GB3836 design; Explosion-proof mark dIICT6, apply to the following IIC level, ignition temperature T6 above, Temperature measurement in the presence of explosive gas. Suitable for use in places with explosive gas danger within the temperature range of dIICT6.
Features
â—‡ Easy to install, multiple temperature ranges can be selected
æ°” Air and liquid, any media compatible with 316L
å¤šç§ A variety of linear analog signal options
å应 Fast response and high accuracy
长期 Long-term stability, low energy consumption, small size
Application area
ç®¡é“ Piping and ventilation systems
液压 Hydraulic and pneumatic systems
å†·å´ Cooling system and heating system
供水 Water supply and hot water system
空调 Air conditioning system
自动化 Automation System Temperature Measurement and Control
Technical Parameters
project name
parameter
Standard range
Measuring range (°C): -50~0; -50~50; 0~50; 0~80;0~100; 0~120; 0~150; 0~200;
Installation method: Insertion depth (mm): 50mm (other than typical thread); can be customized according to user requirements
Probe size (mm): Φ6, Φ8
Technical indicators
sensor
Pt100 or Pt1000
Signal output
4~20mA 0~5VDC 0~10VDC
Signal line specifications
2wire 3wire 3wire
Supply voltage
9~30VDC 9~30VDC 15~30VDC
Accuracy
±0.1%FS ±0.3%FS ±0.5%FS
Pressure resistance
Typical: 40bar (Max: 300bar)
Long-term stability (1 year)
±0.1%FS
Response time
T=50°C 2.3s; T=90°C 5.4s
Electrical protection
Reverse polarity and overload protection, optional surge protection
Ambient temperature
-40~+85°C
Storage temperature
-40~+125°C
Housing material
316 stainless steel
Touch liquid material
316L stainless steel
Protection level
IP65
 Temperature transmitter measurement range
Temperature transmitter measurement range
Why does the temperature transmitter (or analog input card for temperature input in DOS) perform cold junction compensation?
(1) The temperature transmitter is installed on site, and the temperature of the cold end varies with the environment.
(2) When the cold junction is not compensated, the output of the transmitter will be higher than the actual temperature, which will give the operator an erroneous judgment. Therefore, cold junction compensation is required.
What is a cold junction compensator? What is its principle?
The thermocouple reference temperature compensator is a device that automatically compensates for variations in thermocouple measurements due to changes in the reference junction temperature. It is essentially a dc voltage millivolt generator that can produce a change in temperature as the reference temperature changes. When it is connected in series with a thermocouple measuring line, the temperature of the reference terminal can be automatically compensated.
The smart temperature transmitter module is designed for high performance HART protocol temperature transmitters. Supports PT50, PT100, PT500, PT1000 four kinds of thermal resistance and E, J, B, K, N, R, S, T eight thermocouples. It also supports measurement of millivolt signal and resistance signal. Isolated voltage
Transmitter header
DC1000V.
1. Supply voltage: DC10V ~ 32V;
2. Output signal 4-20mA superimposed HART â–¡ protocol digital communication (two-wire system), HART communication does not affect the 4-20mA analog output;
3. It can be remotely managed by the communicator and PC configuration software.
4. Internally use Pt100 to measure the ambient temperature for thermocouple cold junction compensation;
Integrated transmitter
5. Cold end compensation accuracy: 0.5 °C;
6. Damping: 0-32 seconds adjustable;
7. Data refresh rate: 4 times / S;
8. Stability: ± 0.2%/year
9. Operating temperature environment: -40°C~+85°C
(LCD operating temperature range: -20 °C ~ +70 °C);
10. Dimensions: ¢ 44mm;
11. Installation hole spacing: 33mm;
12. Resistance to mechanical vibration: 10 ~ 60HZ, 0.21mm sine wave;
13. Anti-radio frequency interference: IEC61000-4-3, 20V/M, 80~1000MHZ
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
Input signal and range
Integrated temperature transmitter working principle
The integrated temperature transmitter converts the measured temperature of a thermocouple or a thermistor sensor into an electrical signal, and then sends the signal to the input network of the transmitter. This network contains the relevant circuits such as zero adjustment and thermocouple compensation. The zero-adjusted signal is input to the operational amplifier to amplify the signal. The amplified signal is calculated and processed by the V/I converter and then output to a 4-20 mA DC current. The other channel is processed by the A/D converter and displayed on the meter head.
There are two types of transmitter linearization circuits, all using feedback. Thermistor sensors are calibrated with positive feedback, and thermocouple sensors are calibrated with polyline approximation. The integrated digital display temperature transmitter has two display modes. The temperature transmitter of the LCD display is output in a two-wire system, and the temperature transmitter of the LED display is output in a three-wire system.
1, before installation, check whether the accessories are complete, whether there is loose fasteners, tighten the antenna.
2, when installing, pay attention to gently, do not knock, fall. Tighten the antenna to work properly
3. After installation, after the power is turned on, non-operators are prohibited from opening the front cover. If the operator mistakenly operates the front cover, do not save it. After the power is turned off, turn it back on again.
1 Transmitter no output, check the transmitter power is reversed;
The power polarity is connected correctly
2 measuring transmitter power supply, whether there is 24V DC voltage;
It must be ensured that the power supply voltage supplied to the transmitter is ≥12V (ie the voltage at the input of the transmitter power supply is ≥12V). If there is no power, you should check whether the circuit is broken, whether the instrument is selected wrong (input impedance should be ≤ 250Ω); and so on.
3 If it is integrated with the header, check whether the header is damaged (you can short the first two lines of the header, if the short circuit is normal, then the header is damaged);
If the header is damaged, you need to change the header.
4 Connect the current meter into the 24V power supply circuit and check if the current is normal.
If it is normal, the transmitter is normal. At this time, check whether other instruments in the loop are normal.
1, the transmitter power is normal
If it is less than 12 VDC, check whether there is a large load in the loop. The input impedance of the transmitter load should meet RL ≤ (transmitter supply voltage -12V) / (0.02A) Ω
2, whether to conduct integrated debugging
Integrated debugging
3, thermal resistance (or thermocouple) and housing insulation meets the requirements
If insulation is not required, appropriate insulation treatment is required.
1. The heating uses far-infrared stainless steel high-speed heating (2KW × 1) electric heating wire.
2. Humidifying uses external boiler steam humidifier humidification, with energy saving features.
3. With water level automatic compensation, water shortage alarm system.
4. Blackboard temperature: metal blackboard thermometer.
5. Irradiance control: The required irradiance can be obtained by using a radiometer and manually adjusting the power.
6. Irradiance: The average irradiance between 290nm and 800nm ​​wavelength is 550W/m2
7. High temperature, humidity, and light independent systems do not interfere with each other.
1. Two-wire output 4-20mA, strong anti-interference ability;
2. Save the cost of compensation wire and installation temperature transmitter;
3. Safe and reliable, long service life;
4. Cold junction temperature compensation, nonlinear correction circuit.
5. Convert the measured ambient temperature into a single standard DC voltage or DC current output in a linear ratio;
6. Low power consumption and high reliability
7. Excellent anti-interference ability;
8. Pull out the terminal interface, standard rail installation;
9. Small size;
edit
Temperature transmitter technology has been very mature, and it is very common in all factories. Temperature transmitters are often used with some instruments, and there are often some small faults during the matching use. The more common faults and solutions are as follows.
First, the transmitter output does not change when the measured medium temperature rises or falls. This is mostly a problem with the temperature transmitter seal. It may be because the temperature transmitter is not sealed or is not careful when welding. The sensor is soldered with a small hole. This situation generally requires the replacement of the transmitter housing.
Second, the output signal is not stable. This is the reason for the temperature source. The temperature source is an unstable temperature. If the meter display is unstable, that is why the instrument's anti-interference ability is not strong.
Third, the output error of the transmitter is large. The reason for this is more. It may be that the resistance wire of the selected temperature transmitter does not cause the range error, and there may be no calibration when the transmitter is shipped.
1. The error occurs because of leakage or blockage of the three-valve of the temperature transmitter.
2, the temperature transmitter zero position high (or low), resulting in static, differential pressure value is too large (or small), so that the calculated gas volume is larger than the actual gas (or small).
3. The temperature transmitter's accuracy level and range are not correctly selected, or have not been selected according to the requirements of GB/T18603-2001 "Natural Gas Metrology System Technical Requirements" to cause additional errors in measurement.
1. Periodically check the temperature transmitter for leak detection.
2. Regularly check the zero return of the temperature transmitter and find that there is any abnormality or out-of-tolerance condition. It should be calibrated in time and be verified as expired.
3, strictly in accordance with GB/T18603-2001 "natural gas metering system technical requirements" requirements for selection, installation.
4. The winter temperature drops, especially the oil content of the associated gas in the oil field is increased. It is prone to freezing and plugging. The number of blowdowns needs to be increased. The temperature transmitter shall be equipped with insulation equipment (such as adding incubators and heating cables).
The difference of temperature drift: in addition to the basic accuracy of temperature measurement instruments, there are some factors that affect the accuracy of the instrument, such as the change of the working environment causes the accuracy of the instrument to decline. This influence is called the temperature drift of the instrument. This influence is an important indicator of the instrument. The smaller the temperature drift, the higher the measurement accuracy of this instrument is, and it is less affected by changes in the ambient temperature. If the temperature transmitter has the same temperature drift indicator as the digital temperature meter. However, the internal temperature rise of the digital display instrument is greater than that of the temperature transmitter during temperature measurement. Therefore, the effect of the temperature drift of the temperature transmitter on the total accuracy of the instrument is much smaller than that of the digital temperature display instrument.
The difference in accuracy: the accuracy of the temperature transmitter is 0.1%, while the accuracy of the digital display is usually 0.5%. Obviously, the accuracy of the temperature transmitter is 5 times higher than that of the digital display.
Difference in service life: The service life of the 4-20mA two-wire temperature transmitter is much longer than that of the digital temperature meter. The digital power meter's power supply is extremely hot and can easily fail.
The difference in price: usually the price of the temperature transmitter is higher than the price of the digital temperature meter, but the digital temperature meter must be equipped with a protection box in the field, and in order to meet the protection requirements, we must be able to see the value, Only transparent glass can be added. This also adds a lot of cost. There are also digital meters that are not two-wire instruments and require an independent 220V supply. Then you have to pull a power cord from a remote control room and install air. Switch and other safety measures, the overall cost is not low, but increased a lot
The difference in the cost of electricity: temperature transmitter power consumption is less than one-tenth of the digital temperature display instrument, each estimated to be more than a few meters per year power meter temperature saving about 40 degrees.
The difference between installation, maintenance and repair: The temperature transmitter terminal is less than the digital temperature measuring instrument, and the installation and maintenance are convenient. Therefore, the expenses in this respect are also saved.
Summary: Judging from the above differences, it is not appropriate for industrial sites to use indoor digital temperature measuring instruments. Many of its indicators do not meet the requirements of on-site use. The only price is “cheapâ€, but if the overall analysis of the live, it's The price-performance ratio is very poor. The future consumption of electricity and maintenance costs will be very large. [1]
The so-called temperature transmitter is to convert the thermal resistance, thermocouple, resistance and millivolt signal into a standard two-wire system 4...20mA, and transmits the signal to the control room equipment, generally used in the industrial field.
When the range of the traditional temperature transmitter needs to be changed, it is generally adjusted by zeroing and adjusting two potentiometers, but these two potentiometers are the culprits causing large temperature drift of the product. With the advancement of science and technology, due to the cumbersome debugging of traditional analog temperature transmitters and poor comprehensive performance indicators, it has been unable to meet the needs of on-site users, nor can it meet the requirements of factory spare parts, and it is even unable to meet the requirements of the sensor manufacturers for stocking. demand.
Therefore, smart transmitters were born, one of which is to use CUP in the product to digitize the signals, install special software on the PC during debugging, and use data lines and modems to change the range of the temperature transmitter. And the index number; the other is in the smart product itself embedded HART communication board, through the HART protocol communicator to change the temperature transmitter temperature range and index number; there are two kinds of PA agreement and FF agreement The temperature transmitter has a similar principle to the HART protocol. The application of HART, PA, and FF communication protocols makes it easier to program the product (in any location), but it increases the price of the product itself, causing a burden on the owner.
Traditional temperature transmitters, PC-programmed temperature transmitters, and HART-programmed temperature transmitters are the choices for most plants today. However, these methods have been used in the field for many years, and they often hear the user's response to debugging is too cumbersome, not every worker is equipped with a PC, even if there is a PC may not be used, because the debugging software of various manufacturers are not uniform, and very cumbersome Many factories do not have HART communicators. Transmitters are often not very convenient when they need to adjust the range. So is there a product that can change this situation?
From the visit to the idea to the trial production, through nearly 30 months, finally the product passed the assessment of various indicators, in particular, lightning protection and pulse train experiments are very good; also meet the matching needs of on-site users and sensor manufacturers; It is an intelligent product that is easy to operate. It even requires only a screwdriver. Changing the position of the dialer can change its range and make the temperature transmitter a micro-innovation.
1. Two-wire temperature transmitter  . Jie Pei Electronics [Reference date 2016-10-07]
Satin Sheen Elegance: Our Satin Car Wraps exude a refined, low-luster sheen that speaks volumes of understated luxury. The silky finish not only looks exceptional but also feels smooth to the touch, setting your vehicle apart with a touch of class.
Infinite Customization: With a broad spectrum of colors and finishes, our Satin Car Wrap Series invites you to explore your creative side. From timeless Satin Black to custom hues that reflect your personality, the options are endless.
Crafted for Longevity: Crafted from premium vinyl materials, our Satin Car Wraps are engineered to withstand the test of time. They resist fading, brave the elements, and protect against minor imperfections, ensuring your car retains its pristine appearance.
Satin Car Wrap,Satin Wrap Colors,Satin Vinyl Wrap,Satin Wrap
Guangdong HANTAI Decoration Material CO., LTD , https://www.ldcvinyl.com