The word "servo" derives from the Greek word "slave." "Servo motor" can be understood as a motor that absolutely obeys the command signal: the rotor is stationary before the control signal is issued; the rotor rotates immediately when the control signal is issued; the rotor can stop immediately when the control signal disappears.
The servo motor is a micro motor used as an actuator in an automatic control device. Its function is to convert an electric signal into angular displacement or angular velocity of a rotary shaft.
Servo motor is divided into AC servo and DC servo
The basic structure of an AC servo motor is similar to an AC induction motor (asynchronous motor). There are two excitation windings Wf and control winding WcoWf with phase space displacement of 90° electrical angle on the stator, connected to a constant AC voltage, and the purpose of controlling the motor operation is achieved by using the AC voltage or phase change applied to Wc. AC servo motor has characteristics of stable operation, good controllability, fast response, high sensitivity, and non-linearity index of mechanical characteristics and regulation characteristics (requires less than 10% to 15% and less than 15% to 25%, respectively).
The basic structure of a DC servo motor is similar to a general DC motor. Motor speed n = E / K1j = (Ua-IaRa) / K1j, where E is the armature back EMF, K is a constant, j for each pole flux, Ua, Ia for the armature voltage and armature current, Ra is Armature resistance, change Ua or change φ, can control the speed of DC servo motor, but generally use the method of controlling the armature voltage. In the permanent magnet type DC servo motor, the excitation winding is replaced by a permanent magnet, and the magnetic flux φ is constant. . DC servo motors have good linearity and fast time response.
DC servo motor advantages and disadvantages
Advantages: Accurate speed control, very fast torque speed characteristics, simple control principle, easy to use and cheap price.
Disadvantages: Brush commutation, speed limit, additional resistance, wear particles (no dust and explosive environment)

AC servo motor advantages and disadvantages
Advantages: Good speed control, smooth control over the entire speed range, virtually no oscillation, high efficiency above 90%, low heating, high speed control, high accuracy position control (depending on encoder accuracy), rated operating range Internal, constant torque can be achieved, low inertia, low noise, no brush wear, maintenance-free (applicable to clean, explosive environment)
Disadvantages: The control is more complicated, the driver parameters need to be adjusted on-site to determine the PID parameters, and more connection is needed.
DC servo motors are divided into brushed and brushless motors.
Brushed motor has low cost, simple structure, large starting torque, wide speed range, easy control and maintenance, but it is easy to maintain (for carbon brushes), generates electromagnetic interference, has requirements on the use of the environment, and is usually used for cost-sensitive General industrial and civil applications.
The brushless motor is small and light, with large output and fast response, small high-speed inertia, stable torque and smooth rotation, complex control, intelligent, flexible electronic commutation mode, square wave or sine wave commutation, free maintenance of motor, high efficiency and energy saving , Electromagnetic radiation is small, temperature rise is low, long life, suitable for a variety of environments.
AC servo motors are also brushless motors, which are divided into synchronous and asynchronous motors. At present, synchronous motors are generally used in motion control. The power range is large, the power can be large, the inertia is large, the maximum speed is low, and the speed is increased with power. Constant speed drop, suitable for low-speed stable operation.
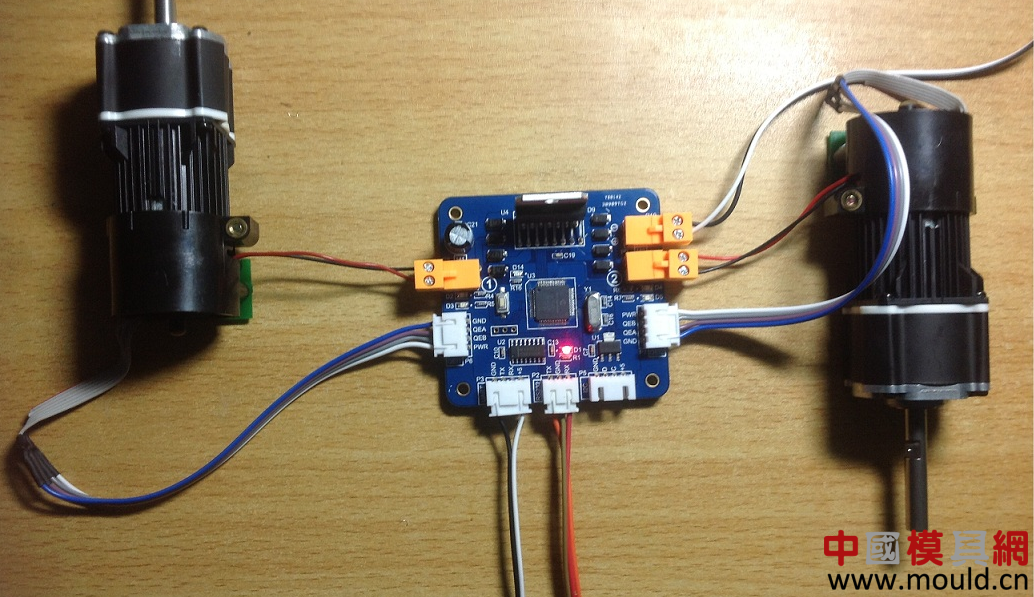
The rotor inside the servo motor is a permanent magnet, and the driver controls the U/V/W three-phase electricity to form an electromagnetic field. The rotor rotates under the action of this magnetic field. At the same time, the motor's own encoder sends the feedback signal to the driver, and the feedback value and target. The values ​​are compared to adjust the rotation angle of the rotor. The accuracy of the servo motor is determined by the encoder accuracy (number of lines).
What is a servo motor? There are several types? What are the characteristics of the job?
A: Servomotors, also known as actuator motors, are used as actuators in automatic control systems to convert received electrical signals into angular displacement or angular velocity output on the motor shaft.
Servo motor is divided into two major categories of DC and AC servo motors. Its main characteristic is that when the signal voltage is zero, there is no rotation phenomenon, and the speed decreases with increasing torque.

What is the difference in performance between AC servo motor and brushless DC servo motor?
A: AC servo motor performance is better, because AC servo is sine wave control, torque ripple is small; and brushless DC servo is trapezoidal wave control. However, brushless DC servo control is relatively simple and inexpensive.
The rapid development of permanent magnet AC servo drive technology makes DC servo system face the crisis of being eliminated.
Since the 1980s, with the development of integrated circuits, power electronics and AC variable speed drive technology, permanent magnet AC servo drive technology has made outstanding development. Well-known electrical companies in various countries have successively introduced new AC servo motors and servo drives. Series products. The AC servo system has become the main development direction of the contemporary high-performance servo system, making the DC servo system face the crisis of being eliminated.
Permanent magnet AC servo motor compared with DC servo motor, the main advantages are:
(1) No brush and commutator, more reliable operation and maintenance-free.
(2) Stator winding heating is greatly reduced.
(3) Inertia is small, and the system has quick response.
(4) High speed and high torque work well.
(5) Small size and light weight at the same power.
The Rise and Status of Permanent Magnet AC Servo System
Since the Indramat Division of Rexroth GmbH of MANENSMANN in Germany officially launched the MAC Permanent Magnet AC Servo Motor Drive System at the 1978 Trade Fair, marking the beginning of a new generation of AC servo technology. By the mid- to late 1980s, major companies had already had a complete series of products, and the entire servo device market had turned to an exchange system. The early simulation system has some shortcomings such as zero drift, anti-jamming, reliability, accuracy, and flexibility. It has not yet fully satisfied the requirements of motion control. In recent years, it has been used with microprocessors and new digital signal processors (DSPs). A digital control system has appeared and the control part can be completed by software. Since the 1990s, all-digital sine-wave controlled permanent magnet AC servo motor drive system has further increased its position in the field of transmission.
At present, high-performance electrical servo systems mostly use permanent-magnet synchronous AC servo motors, and control drivers often use fast, accurate all-digital position servo systems. Typical manufacturers include Siemens of Germany, Kollmorgen of the United States, and Panasonic and Yaskawa of Japan.
AC servo motor
The construction of the AC servo motor stator is basically similar to that of a capacitor-separated single-phase asynchronous motor. The stator is equipped with two windings that are mutually different by 90°, one is the field winding Rf, which is always connected to the alternating voltage Uf, and the other is the control winding L, which is connected to the control signal voltage Uc. Therefore, the AC servo motor is also called two servo motors.
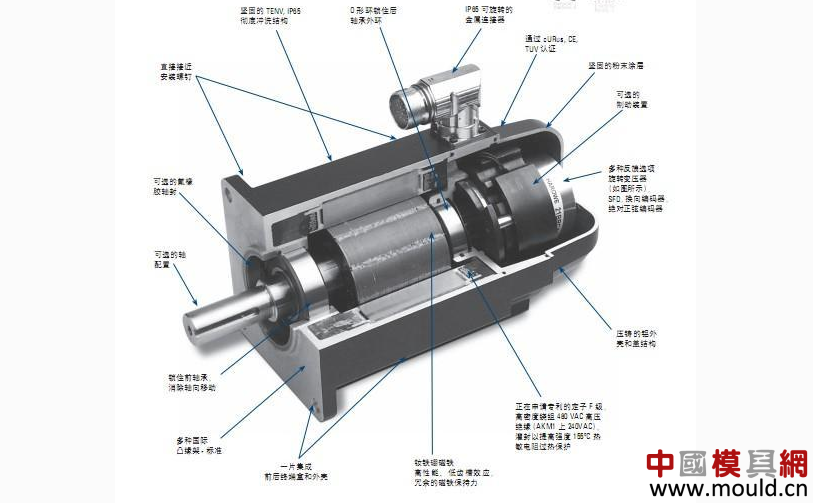
The rotor of the AC servo motor is usually made into a squirrel cage type, but in order to enable the servo motor to have a wide speed range, linear mechanical characteristics, no "rotation" phenomenon and fast response performance, it should have a comparison with an ordinary motor. Rotor resistance and small moment of inertia of these two features. At present, there are two types of rotor structures that are widely used: one is a squirrel cage rotor made of a high-resistivity conductive material made of a high-resistivity conductive material. In order to reduce the rotor's rotational inertia, the rotor is made slender; One is a hollow cup-shaped rotor made of aluminum alloy. The cup wall is only 0.2-0.3mm. The hollow cup-shaped rotor has a small moment of inertia, rapid response, and stable operation, so it is widely used.
When there is no control voltage in the AC servo motor, only the pulsating magnetic field generated by the excitation winding in the stator, and the rotor is stationary. When there is a control voltage, a rotating magnetic field is generated in the stator, and the rotor rotates in the direction of the rotating magnetic field. Under a constant load, the rotational speed of the motor varies with the magnitude of the control voltage. When the phase of the control voltage is opposite, the servo motor Will reverse.
Although the operating principle of the AC servo motor is similar to that of the capacitor-operated single-phase asynchronous motor, the rotor resistance of the former is much larger than that of the latter, so the servo motor has three remarkable features compared to the capacitor-running asynchronous motor:
1. Large starting torque: Due to large rotor resistance, the torque characteristics (mechanical characteristics) are closer to linear, and the starting torque is larger. Therefore, when the stator has a control voltage, the rotor rotates immediately, which means that it has a quick startup and high sensitivity.
2. Wide operating range: stable operation and low noise.
3, no rotation phenomenon: the running servo motor, as long as the loss of control voltage, the motor immediately stop running.

What is called "precision transmission micro motor"?
"Precision transmission micro motor" can quickly and correctly execute frequently-changed commands in the system to drive servos to complete the expected tasks. Most of them can meet the following requirements:
1. It can be frequently started, stopped, braked, reversed and run at low speed. It has high mechanical strength, high heat-resistant grade and high insulation grade.
2, fast corresponding ability is good, the torque is larger, the moment of inertia is small, the time constant is small.
3, with a driver and controller (such as servo motor, stepper motor), control performance is good.
4, high reliability, high precision.
Classification, Structure and Performance of "Precision Transmission Micromotors"
1, AC servo motor
(1) Cage-type two-phase AC servomotors (slender-cage rotors, approximately linear mechanical characteristics, small volume and excitation current, low-power servo, and low speed operation are not smooth enough).
(2) Non-magnetic cup rotor two-phase AC servo motor (narrow cup rotor, approximately linear mechanical characteristics, large volume and excitation current, low power servo, smooth running at low speed).
(3) Ferromagnetic cup rotor two-phase AC servo motor (ferromagnetic cup-type rotor, approximately linear mechanical characteristics, large rotor inertia, small cogging, stable operation).
(4) Synchronous permanent-magnet AC servo motor (combination of permanent magnet synchronous motor, tachometer and position detection element coaxial unit, stator is 3-phase or 2-phase, magnetic material rotor, must be equipped with a drive; wide speed range, mechanical The characteristic consists of a constant torque zone and a constant power zone, which can be continuously blocked, fast corresponding performance is good, output power is large, torque fluctuation is small; there are two methods of square wave drive and sine wave drive, and the control performance is good. Products.
(5) Asynchronous three-phase AC servo motor (similar to the rotor and cage asynchronous motor, must be equipped with a drive, vector control, extended constant power speed range, mostly used for machine tool spindle speed control system).
2, DC servo motor
(1) Printed winding DC servo motor (disc rotor, disc stator axially bonded columnar magnet, small rotor inertia, no cogging effect, no saturation effect, large output torque).
(2) Wire-wound disc DC servo motor (disc rotor, stator axially bonded columnar magnet, small rotor inertia, superior control performance than other DC servo motors, high efficiency, large output torque).
(3) Cup-type armature permanent magnet DC motor (hollow cup rotor, small rotor inertia, suitable for incremental motion servo system).
(4) Brushless DC servo motor (The stator is polyphase winding, the rotor is permanent magnet, with rotor position sensor, no spark interference, long life, low noise).
3, torque motor
(1) DC torque motor (flat structure, number of poles, number of commutation segments, number of series conductors, large output torque, continuous operation at low speed or locked rotor, good mechanical and control characteristics, and low electromechanical time constant).
(2) Brushless DC torque motors (similar in structure to brushless DC servo motors, but flat, with many poles and number of series conductors in series; large output torque, good mechanical and control characteristics, long life, no spark, no noise low).
(3) Cage type AC torque motor (Cage rotor, flat structure, with a large number of poles, large starting torque, small electromechanical time constant, long-term stalled operation, and relatively soft mechanical characteristics).
(4) Solid rotor AC torque motor (solid rotor of ferromagnetic material, flat structure, a large number of poles, can be locked for a long time, running smoothly, the mechanical properties are soft).
4, stepping motor
(1) Reactive stepping motor (fixed rotors are all laminated by silicon steel sheet, there is no winding on the rotor core, there are control windings on the stator; small step angle, high starting and running frequency, step angle accuracy is low, no Self-locking torque).
(2) Permanent-magnet stepper motor (permanent-magnet rotor, radial magnetization polarity; large step angle, low start-up and running frequency, maintaining torque, less power consumption than the reactive type, but with positive and negative pulses Current).
(3) Hybrid stepper motor (permanent magnet rotor, axial magnetization polarity; high step angle accuracy, holding torque, small input current, both reaction type and permanent magnet type advantages).
5. Switched reluctance motors (fixed rotors are all laminated by silicon steel sheets, all of which are salient-pole type. Large-step-response stepper motors with pole numbers are similar in structure, with a rotor position sensor, torque direction and current The direction is irrelevant, the speed range is small, and the noise is large. The mechanical characteristics consist of constant torque zone, constant power zone, and series excitation characteristic zone.
6, linear motor (structure is simple, rails, etc. can be used as a secondary conductor, suitable for linear reciprocating motion; high-speed servo performance, power factor and high efficiency, excellent performance at constant speed).
Cnc Turning Parts,Lathe Chips Remover,Lathe Chip Removal,Cnc Lathe Chips Remover
Ningbo junfa CNC Equipment Co. Ltd. , https://www.nbintimecnc.com