In general, CNC horizontal lathes with a maximum turning diameter of 200 to 1000 mm and a maximum turning length of up to 5000 mm are usually subjected to the following operations and function tests.
1, manual function test:
The machine tool is tested for functionality with buttons, switches or manual controls to test its flexibility, smoothness and reliability.
(1) Select one of the spindle speed and the spindle speed of the power tool to start the continuous test of forward rotation, reverse rotation, and stop (including braking) with the spindle and the power tool rest mechanism. The continuous operation is not less than 7 times.
(2) Spindle and power tool spindle do low, medium and high speed rotation test. The difference between the speed command value and the displayed value (or measured value) must not exceed 5%.
(3) Optionally, one kind of feed amount, which will continuously start the feed and stop action, and perform the work feed and rapid feed test on the full stroke of the Z-axis, X-axis, and C-axis, Z-axis, X The fast stroke of the shaft should be greater than 1/2 full stroke. No less than 7 consecutive operations in the opposite direction. And measure the rapid feed speed and acceleration and deceleration characteristics. Test the fluctuation of servo motor current, its allowable difference is stipulated by the manufacturer.
(4) Perform low, medium, and high feedrate conversion tests on all strokes of the Z-axis, X-axis, and C-axis.
(5) Feed test by hand pulse generator or single-step moving carriage, slide plate, C' axis.
(6) Manually or maneuvering the tailstock and tailstock spindles for motion inspection on their full travel.
(7) The moving parts of the locking mechanism are used for the locking test at any position of its full stroke. The slides of the inclined and vertical guides shall not fall after cutting off the power.
(8) Rotary tool holders perform a variety of indexing and clamping tests.
(9) Hydraulic, lubrication, and cooling systems do seal, lubrication, and cooling performance tests, requiring easy adjustment, flexible operation, good lubrication, adequate cooling, and no leakage of the systems.
(10), chip evacuation, debris removal device inspection.
(11) Machines with automatic tool changer and tool changer should perform automatic tool change and tool change inspection.
(12) The C' axis of the indexing mechanism shall be indexed and positioned.
(13) Function tests of various indicators, program reading devices, and ventilation systems of digital control devices.
(14) The chuck is clamped and loosened to check its flexibility and reliability.
(15), machine tool safety, insurance, functional inspection of protective devices;
(16) Measure the braking time at the maximum rotation speed of the spindle and take the average of 7 times;
(17), automatic monitoring, automatic knife setting, automatic measurement, automatic loading and unloading device and other auxiliary functions;
(18), hydraulic lubrication, cooling system to do sealing, lubrication, cooling performance inspection, requires easy operation, flexible action, good lubrication, adequate cooling, no leakage of the system.
2, control function acceptance
Use the CNC control command to check the function of the machine to verify its flexibility and functional reliability.
(1) Spindle rotates forward, reverses, stops and changes spindle speed test (stepless speed change mechanism does low, medium and high speed inspection; stepless speed change mechanism does all levels of speed check);
(2) Feeding agencies do low, medium and high feeds and rapid feed change tests;
(3), C' axis, X axis and Z axis linkage test;
(4) Rotary tool holders are used to carry out various displacement clamping tests. One station is selected to measure the adjacent tool position and the rotation time of the rotation 1800, and the average value is 7 consecutive times.
(5) Test feed coordinate overtravel, manual data input, coordinate position display, return reference point, program number indication and search, program stop, program end, program elimination, single step feed, linear interpolation, round Arc plate interpolation, linear cutting cycle, taper cutting cycle, thread cutting cycle, circular arc cutting cycle, tool position compensation, pitch compensation, gap interpolation, and other specifications specified by the reliability of the panel and program functions and the flexibility of the action;
3, temperature rise test
Measure the temperature rise of the main shaft bearings, lubricating oil, and other major heat sources during high-speed and medium-speed operation of the main shaft and their variations. Inspection should be connected
Continue to operate for 180 minutes. In order to ensure that the machine tool starts testing in the cold state, it must not be operated within 16 hours before the test. The test shall not stop midway. Before the test, the quantity and brand of the lubricating oil should be checked and the requirements of the instruction manual should be met.
Temperature measurements should be made at the spindle bearings (front, center, rear) and where the spindle housing, motor housing, and hydraulic tank generate heat.
The spindle runs continuously and is measured every 15 minutes. Finally, the time-temperature rise curve is plotted with the temperature value of the measured part, and the temperature rise value for 180 minutes is used as assessment data.
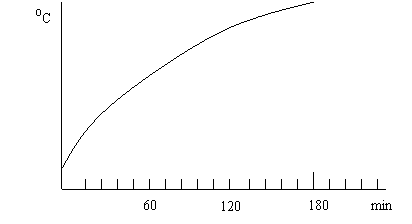
Time-temperature rise graph
In the actual inspection process, the following points should be noted:
(1) Temperature measurement points should be selected as close as possible to the position of the part under test. The bearing temperature of the spindle should be measured at the temperature measurement process hole. In the machine tool without temperature measuring process holes, a thermocouple may be installed in the fastening screw holes of the front and rear flanges of the spindle, and the screw holes are filled with grease, and the holes are sealed with a rubber mud or a plastic cloth;
(2) The room temperature measuring point should be located at any height of 500 mm from the center of the machine tool. The measuring point of the fuel tank should be as close as possible to the suction port.
1. Raw material pulverization: Raw materials are mainly divided into two categories, starch and fat. Starch is mainly various grains. Its pulverization can be achieved by ordinary pulverizers. It only needs to ensure the fineness and clean raw materials during the pulverization process. Hygiene can be. Use a colloid mill to pulverize into separate packs or puree, and the meat only needs to be pulverized into meat puree or powder with a colloid mill, and then added to the grain powder and stirred evenly.
2. Raw material mixing: The mixing equipment has two functions, one is to mix all kinds of raw materials evenly, and the other is to adjust the moisture and humidity. It is generally a vertical rapid mixer: the mixing time is short, the mixing is completed quickly, and the machine is used before the humidity of the raw material changes significantly, which ensures the uniformity and quality of the puffing of the dog food particles. The disadvantage is: the single-cylinder mixing capacity is small, and it needs to be stirred all the time during the production process.
3. Raw material extrusion, puffing and curing molding: The twin-screw extruder extrudes and extrudes under high temperature and high pressure, and produces dog food and cat food particles of different styles and shapes by changing different molds. For different raw material ratios and humidity, it is necessary to adjust the temperature and screw speed of different regions and the feeding speed of the feeder to ensure that the produced dog food particles are of high quality and good appearance.
Pet food production line,Dog food production line,Cat food production line
Jump Machinery (Shanghai) Limited , https://www.shanghaimachineres.com